26th of March at 16h00, Sadaf Azimi and Iury Araujo will give two short presentations, to promote discussion on two relevant ongoing or disruptive topics. Afterwards, there will be a social gathering where everyone can talk freely on whatever subjects they like.
Location: G4.1Online: https://videoconf-colibri.zoom.us/j/97404078835?pwd=7iIG7YqLwXgZU5g7QHZKFbuAMyInqb.1
Sadaf Azimi – “A Systematic Review on Smart Contracts Security Design Patterns”
Bio
Sadaf Azimi is an IT professional with Over 11 years of experience as an IT Lecturer and as an analyst and developer of medium-scale projects in the area of IT Systems, such as marketing software and warehouse management. She graduated with a bachelor’s degree in Computer Engineering (Software) from the Islamic Azad University of Tuyserkan in February 2008 in Iran. Later, she got her two-year master‘s degree in Knowledge Management from Malaysia Multimedia University in June 2012 in Malaysia.She continued her academic journey in 2022, enrolling in the doctoral program in Informatics Engineering at the University of Coimbra. Her research for her Ph.D. focuses on addressing the security in smart contracts by conducting a thorough analysis of the known security vulnerabilities, identifying design patterns that can mitigate these risks, proposing new security design patterns to fill gaps, and using software metrics as an indicator of software quality to help developers implement more secure smart contracts. Furthermore, her research aims to evaluate and benchmark the effectiveness of existing static vulnerability detection tools. She seeks to contribute to the field of blockchain and smart contract security, ultimately enhancing the security and reliability of smart contracts in real-world applications.
Abstract
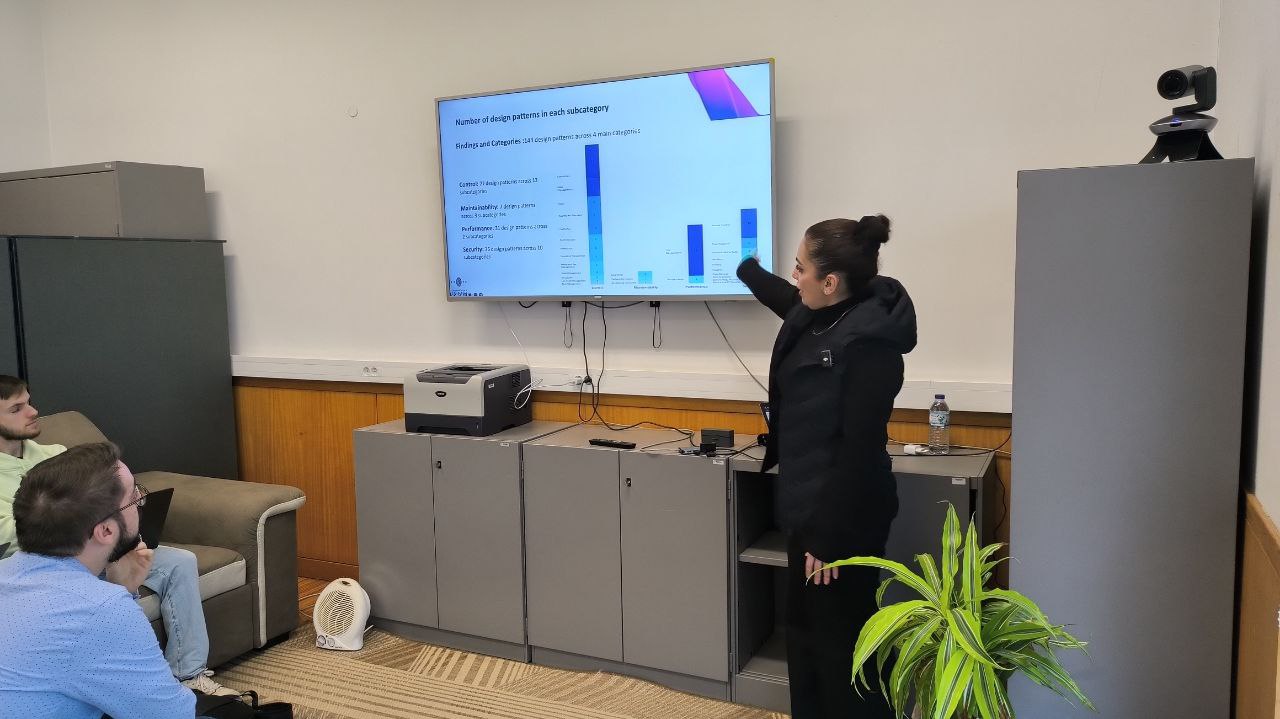
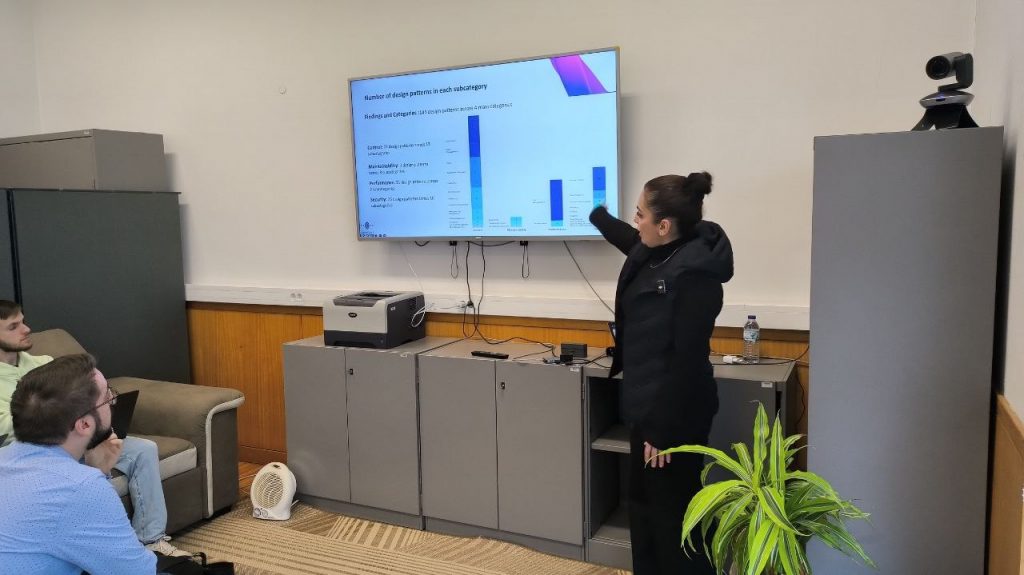
Smart contracts have accelerated the adoption of blockchain technology across various domains by enabling coded agreements between transaction participants. However, increased software defects and vulnerabilities in smart contracts, driven by developer inexperience with languages like Solidity and a lack of effective detection tools, pose significant risks. Given the high value of assets managed on blockchain, these vulnerabilities can lead to severe consequences.Researchers and practitioners have proposed numerous smart contract design patterns to mitigate certain faults or vulnerabilities. Despite these efforts, it remains unclear which types of defects these patterns target and how effectively they address the wide range of existing smart contract security vulnerabilities. In this paper, we review the state of the art in smart contract design patterns, categorizing them and analyzing their effectiveness in mitigating known security vulnerabilities. Our findings reveal that only five patterns directly aim to prevent security vulnerabilities, collectively addressing just 6 out of 94 security issues identified by OpenSCV, highlighting the need for further research on smart contract security design patterns.
Iury Araujo – “Enhancing Intrusion Detection in Containerized Services: Assessing Machine Learning Models and an Advanced Representation for System Call Data”
Bio
Iury holds a BSc degree in Computer Science and a MSc in Informatics from the Federal University of Paraíba, Brazil. He is pursuing a PhD in Informatics Engineering at the University of Coimbra, Portugal, focusing on intrusion detection in containerized services based on machine learning.
Abstract
Security is a fundamental requirement for modern digital systems, particularly in environments such as cloud computing, IoT, and microservices. Intrusion Detection Systems play a crucial role in identifying and mitigating threats, yet securing containerized services remains a significant challenge due to their architecture and shared resource dependencies. This presentation will explore a machine learning-based approach to enhance intrusion detection in containerized environments. We introduce a novel graph-based representation of system calls to preserve contextual relationships, improving detection performance while maintaining low false alarm rates. Additionally, a sliding window-based post-processing phase further refines detection.